2020年6月2日
GCC - まとめリンク
目次: GCC
GCCについて。
- GCCを調べる - その1 - ビルド
- GCCを調べる - その2 - デバッグ環境
- GCCを調べる - その3 - RTL (Register Transfer Language) の出力
- GCCを調べる - その4 - RTL (Register Transfer Language) を眺める
- GCCを調べる - その5 - RTL (Register Transfer Language) の定義
- GCCを調べる - その6 - ベクトルレジスタ用のregister constraintを足す
- GCCを調べる - その7 - machine mode定義ファイルの場所
- GCCを調べる - その8-1 - ベクトルレジスタ定義を足す
- GCCを調べる - その8-2 - レジスタとレジスタクラス
- GCCを調べる - その8-3 - レジスタconstraint判定
- GCCを調べる - その9 - ベクトル型用マシンモードの追加
- GCCを調べる - その10-1 - ベクトル型を使うとエラー(TARGET_VECTOR_MODE_SUPPORTED_P追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その10-2 - ベクトル型への対応(TARGET_VECTOR_MODE_SUPPORTED_P追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その11-1 - オプションO0のエラー調査(define_expand追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その11-2 - オプションO0のエラーを引き起こすRTL(define_expand追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その11-3 - エラーを引き起こすRTLを回避する(define_expand追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その12-1 - 続、オプションO0のエラー調査(define_insn追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その12-2 - ベクトル命令の出力(define_insn追加編)
- GCCを調べる - その13-1 - オフセット付きアドレスを禁止する
- GCCを調べる - その13-2 - オフセット付きアドレス全部禁止
- GCCを調べる - その13-3 - オフセット付きアドレスの分割
- GCCを調べる - その13-4 - ベクトル命令のオフセット付きアドレスだけを禁止
- GCCを調べる - その14-1 - genopinitとexpandとenum optab_tag
- GCCを調べる - その14-2 - genopinitとexpandとpats[].scode
- GCCを調べる - その15-1 - 浮動小数点のロードストアになぜかベクトルレジスタが出現する
- GCCを調べる - その15-2 - ベクトルレジスタが選ばれてしまう原因追跡
- GCCを調べる - その15-3 - ベクトルレジスタを使用するmachine mode
- GCCを調べる - その16 - 自動ベクトル化を有効にする
- GCCを調べる - その17 - ベクトル四則演算、論理演算の定義
- GCCを調べる - その18 - ベクトルNot演算の定義
- GCCを調べる - memmoveのfoldingその1
- GCCを調べる - memmoveのfoldingその2
- GCCを調べる - memmoveのfoldingその3
- GCCを調べる - デバッグ環境再び
- GCCを調べる - デバッグ環境再び(ブートストラップモード)
- GCCを調べる - GCC 8.3のfoldingバグ - 発生条件
- GCCを調べる - GCC 8.3のfoldingバグ - エラーの原因をvuseから追う
- GCCを調べる - GCC 8.3のfoldingバグ - GCC 9.1との比較
- GCCを調べる - GCC 8.3のfoldingバグ - 解決編
- volatileをnon-volatileで参照してはいけない
GCCを含めたツールチェーンについて。
- Armadillo-9用のクロスコンパイル環境
- CodeSourceryに代わってLinaroのARMクロスコンパイラを使う
- ARM向けクロスコンパイラを自分でビルド
- Ubuntu 14.04とccacheとGCC 7
- Ubuntu 14.04のccacheの謎
- AArch64向けLinux開発環境の構築 その1
- AArch64向けLinux開発環境の構築 その2
- RISC-V向けクロスコンパイラ
- RISC-V 64向けLinux開発環境の構築
- GCCがない世界はどうなるか?
- クロスビルド用ツールチェーン - その1
- クロスビルド用ツールチェーン - その2
- クロスビルド用ツールチェーン - GCC 10.0にしたらハマった
- FSF Copyright Assignment
- freestandingとnostdlib
- nostdlibとnostartfiles
- AArch64向けLinuxデバッグ環境の構築
- fno-builtinによるlibc関数呼び出し最適化の抑制
- クロスビルド用ツールチェーン - なぜか必要なsysroot/usr/lib
目次: 一覧の一覧
- Ubuntu 14.04のccacheの謎
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年6月1日
GCCを調べる - その13-4 - ベクトル命令のオフセット付きアドレスだけを禁止
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月31日の日記参照)見たとおり、メモリというかオフセット付きアドレスを全部禁止するのは明らかにやりすぎで、他の命令に悪影響を及ぼしていました。スカラ命令はオフセット付きアドレスを許可し、ベクトル命令だけオフセット付きアドレスを禁止したいところです。
オペランドを許可する、しないを判断するコードを改造すればできるでしょうか?コードを見てみます。
constraint "m" の定義(再掲)
// gcc/common.md
(define_memory_constraint "TARGET_MEM_CONSTRAINT"
"Matches any valid memory."
(and (match_code "mem")
(match_test "memory_address_addr_space_p (GET_MODE (op), XEXP (op, 0),
MEM_ADDR_SPACE (op))")))
constraint "m" の条件判定コード
// gcc/recog.c
//★★各引数の値
//mode = E_V64SImode
//addr = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//as = 0
int
memory_address_addr_space_p (machine_mode mode ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx addr, addr_space_t as)
{
#ifdef GO_IF_LEGITIMATE_ADDRESS
...
#else
return targetm.addr_space.legitimate_address_p (mode, addr, 0, as);
#endif
}
// gcc/targhook.c
//★★各引数の値
//mode = E_V64SImode
//mem = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//strict = 0
//as = 0
bool
default_addr_space_legitimate_address_p (machine_mode mode, rtx mem,
bool strict,
addr_space_t as ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
return targetm.legitimate_address_p (mode, mem, strict);
}
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
#undef TARGET_LEGITIMATE_ADDRESS_P
#define TARGET_LEGITIMATE_ADDRESS_P riscv_legitimate_address_p
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
//★★各引数の値
//mode = E_V64SImode
//mem = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//strict_p = 0
static bool
riscv_legitimate_address_p (machine_mode mode, rtx x, bool strict_p)
{
struct riscv_address_info addr;
return riscv_classify_address (&addr, x, mode, strict_p);
}
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
//★★各引数の値
//x = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//mode = E_V64SImode
//strict_p = 0
static bool
riscv_classify_address (struct riscv_address_info *info, rtx x,
machine_mode mode, bool strict_p)
{
switch (GET_CODE (x))
{
...
case PLUS:
info->type = ADDRESS_REG;
info->reg = XEXP (x, 0);
info->offset = XEXP (x, 1);
//★★各変数の値
//info->reg = x->u.fld[0].rt_rtx = (reg/f:SI 108)
//info->offset = x->u.fld[1].rt_rtx = (const_int 256 [0x100])
return (riscv_valid_base_register_p (info->reg, mode, strict_p)
&& riscv_valid_offset_p (info->offset, mode));
...
}
}
関数memory_address_addr_space_p() のaddrを見ると、メモリアドレスを表すRTLしか渡されません。この情報だけではスカラ命令のオペランドか、ベクトル命令のオペランドか、判断するのは困難です。
ベクトル命令はmachine modeがV64SIであることを利用するとうまくいくかもしれません。関数riscv_classify_address() を変更し、mode == V64SIだったらPLUSなどREG以外を使ったRTLに対しfalseを返せば良さそうです。
mode == V64SIのときfalseを返す
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
//★★各引数の値
//x = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//mode = E_V64SImode
//strict_p = 0
static bool
riscv_classify_address (struct riscv_address_info *info, rtx x,
machine_mode mode, bool strict_p)
{
switch (GET_CODE (x))
{
...
case PLUS:
if (mode == E_V64SImode) //★★machine modeがV64SIならオフセット付きアドレスは許可しない
return false;
info->type = ADDRESS_REG;
info->reg = XEXP (x, 0);
info->offset = XEXP (x, 1);
return (riscv_valid_base_register_p (info->reg, mode, strict_p)
&& riscv_valid_offset_p (info->offset, mode));
...
}
}
mode == V64SIのときfalseを返す変更を加えたとき、アセンブラの差分
$ diff -u b_before.s b_mod.s
--- b_before.s 2020-05-28 21:17:24.607184754 +0900
+++ b_mod.s 2020-05-30 22:37:02.370663628 +0900
@@ -35,7 +35,8 @@
# 0 "" 2
#NO_APP
- vsw.v v0,256(a5)
+ addi a4,a5,256
+ vsw.v v0,0(a4)
.loc 1 9 2
addi a4,s0,-336
#APP
結果だけ見ると良さそうですが、将来的にオフセットアドレスが使えるベクトル命令が出てきたときに、判別不能になり困ります。その場しのぎ感が否めません。もっと良い方法はあるでしょうか?
もっと簡単な方法
実はもっと簡単な方法で対処できます。変更すべき箇所については、この取り組みの発端「constraint "m" をチェックしていそうな箇所から調査を開始した」ことを思い出していただければ想像が付くと思います。constraint "m" を使っている箇所はdefine_insnです。
追加したdefine_insn(再掲)
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md
(define_attr "vecmode" "unknown,V64SI"
(const_string "unknown"))
(define_insn "*movv64si_internal"
[(set (match_operand:V64SI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "=v,v,m")
(match_operand:V64SI 1 "move_operand" " v,m,v"))] //★★constraint "m" を使っている場所
"(register_operand (operands[0], V64SImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], V64SImode))" return riscv_output_move (operands[0], operands[1]);
[(set_attr "move_type" "move,load,store")
(set_attr "vecmode" "V64SI")])
この "m" を変更して、オフセット付きアドレスオペランドだけを拒否したいですが、そんな都合の良いconstraintはあるでしょうか?実はRISC-Vには既にあります。constraint "A" です。
constraint "A" の定義
;; gcc/config/riscv/constraints.md
(define_memory_constraint "A"
"An address that is held in a general-purpose register."
(and (match_code "mem")
(match_test "GET_CODE(XEXP(op,0)) == REG")))
コードを見ると、constraint "A" が見ている条件は、種別がメモリであり、オペランドがREG(オフセットありだとPLUSなどになる)であることです。先程の改造と同じ発想ですね。mをAに変更します。
変更後のdefine_insn
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md
(define_insn "*movv64si_internal"
[(set (match_operand:V64SI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "=v,v,A")
(match_operand:V64SI 1 "move_operand" " v,A,v"))] //★★constraint "A" に変更
...
constraint "A" を使ったとき、アセンブラの差分
$ diff -u b_before.s b_final.s
--- b_before.s 2020-05-28 21:17:24.607184754 +0900
+++ b_final.s 2020-05-28 21:20:20.219175573 +0900
@@ -35,7 +35,8 @@
# 0 "" 2
#NO_APP
- vsw.v v0,256(a5)
+ addi a4,a5,256
+ vsw.v v0,0(a4)
.loc 1 9 2
addi a4,s0,-336
#APP
出力結果のアセンブリも良い感じですし、ビルドの際にアセンブラも文句を言わなくなりました。
長きに渡りましたが、やっとベクトル型を使ったGCC拡張インラインアセンブラが書けるようになりました。良かった良かった。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月31日
GCCを調べる - その13-3 - オフセット付きアドレスの分割
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月30日の日記参照)見たとおり、関数process_alt_operands() がグローバル変数goal_alt_winを変更しました。
フラグの変更が呼び出し元のcurr_insn_transform() にどう影響するか調べます。RTLが変化するところに、適宜コメントを入れました。
goal_alt_winの影響
// gcc/lra-constraints.c
static bool
curr_insn_transform (bool check_only_p)
{
...
if (process_alt_operands (reused_alternative_num))
alt_p = true;
...
n_outputs = 0;
outputs[0] = -1;
for (i = 0; i < n_operands; i++)
{
int regno;
bool optional_p = false;
rtx old, new_reg;
rtx op = *curr_id->operand_loc[i];
//★★goal_alt_win = {false, true, }
if (goal_alt_win[i]) //★★i = 0メモリオペランドのときは成立しない
{
...
}
//★★goal_alt_matches = {-1, -1, }
/* Operands that match previous ones have already been handled. */
if (goal_alt_matches[i] >= 0) //★★成立しない
continue;
//★★goal_alt_matched[i] = {-1, -47, ...}
//★★goal_alt_offmemok = {true, false, }
/* We should not have an operand with a non-offsettable address
appearing where an offsettable address will do. It also may
be a case when the address should be special in other words
not a general one (e.g. it needs no index reg). */
if (goal_alt_matched[i][0] == -1 && goal_alt_offmemok[i] && MEM_P (op)) //★★成立する
{
enum reg_class rclass;
rtx *loc = &XEXP (op, 0);
enum rtx_code code = GET_CODE (*loc);
push_to_sequence (before);
rclass = base_reg_class (GET_MODE (op), MEM_ADDR_SPACE (op),
MEM, SCRATCH);
if (GET_RTX_CLASS (code) == RTX_AUTOINC)
new_reg = emit_inc (rclass, *loc, *loc,
/* This value does not matter for MODIFY. */
GET_MODE_SIZE (GET_MODE (op)));
else if (get_reload_reg (OP_IN, Pmode, *loc, rclass, FALSE,
"offsetable address", &new_reg)) //★★オフセットの設定が2つのRTLに分割される
{
rtx addr = *loc;
enum rtx_code code = GET_CODE (addr);
if (code == AND && CONST_INT_P (XEXP (addr, 1)))
/* (and ... (const_int -X)) is used to align to X bytes. */
addr = XEXP (*loc, 0);
lra_emit_move (new_reg, addr); //★★ベースレジスタにオフセットを加算するRTLを作成
//★★こんなのが作成される
//(insn 22 0 0 (set (reg:SI 114)
// (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))) 3 {addsi3}
// (nil))
if (addr != *loc)
emit_move_insn (new_reg, gen_rtx_AND (GET_MODE (new_reg), new_reg, XEXP (*loc, 1)));
}
before = get_insns ();
end_sequence ();
//★★*locとnew_regの値
//
//*loc = (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100]))
//
//new_reg = (reg:SI 114)
//★★Before:
// ↓このRTL plusがregに置き換わる
//(insn 10 11 13 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
// (const_int 256 [0x100])) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
// (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":8:2 134 {*movv64si_internal}
// (expr_list:REG_DEAD (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
// (nil)))
//
//★★After:
//
//(insn 10 11 13 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg:SI 114) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
// (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":8:2 134 {*movv64si_internal}
// (expr_list:REG_DEAD (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
// (nil)))
*loc = new_reg;
lra_update_dup (curr_id, i);
}
...
lra_process_new_insns (curr_insn, before, after, "Inserting insn reload"); //★★オフセットを事前計算するRTLが追加される
return change_p;
}
最後のlra_process_new_insns() はちょっとややこしくて、1つ目の引数(curr_insn)の前に2つ目の引数(before)のRTLを足し、後ろに3つ目の引数を(after)を足す関数です。図示したほうがわかりやすいですね。
- 呼び出し前: (curr_insn)
- 呼び出し後: (before) (curr_insn) (after)
関数呼び出し前後のRTLの中身を下記に示します。今回はafterはNULLなので、curr_insnの後ろには何も足されません。
lra_process_new_insns() の前
(insn 21 7 11 2 (set (reg:SI 113)
(plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -376 [0xfffffffffffffe88]))) "b.c":8:2 3 {addsi3}
(nil))
(insn 11 21 10 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (reg:SI 113) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:8)
]
[] b.c:8)) "b.c":8:2 -1
(nil))
★curr_insnは↓のRTLを指している
(insn 10 11 13 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg:SI 114) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048]) ★*loc = new_reg; でオペランド変更済み
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":8:2 134 {*movv64si_internal}
(expr_list:REG_DEAD (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(nil)))
(insn 13 10 12 2 (set (reg:V64SI 110 [ v2 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -336 [0xfffffffffffffeb0])) [1 b+80 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:9)
]
[] b.c:9)) "b.c":9:2 -1
(nil))
...
lra_process_new_insns() の後
(insn 21 7 11 2 (set (reg:SI 113)
(plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -376 [0xfffffffffffffe88]))) "b.c":8:2 3 {addsi3}
(nil))
(insn 11 21 22 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (reg:SI 113) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:8)
]
[] b.c:8)) "b.c":8:2 -1
(nil))
★beforeは↓のRTLを指している
(insn 22 11 10 2 (set (reg:SI 114) ★このRTLが追加された(事前にアドレスを格納するレジスタにオフセットを足すため)
(plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 256 [0x100]))) "b.c":8:2 3 {addsi3}
(nil))
★curr_insnは↓のRTLを指している
(insn 10 22 13 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg:SI 114) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":8:2 134 {*movv64si_internal}
(expr_list:REG_DEAD (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(nil)))
(insn 13 10 12 2 (set (reg:V64SI 110 [ v2 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -336 [0xfffffffffffffeb0])) [1 b+80 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:9)
]
[] b.c:9)) "b.c":9:2 -1
(nil))
...
ベクトル命令のRTLの前にアドレスを計算するRTLが出力されました。うまくいってそうです。
うまくいっているけど、もう一息
話が長くなってきて忘れてしまいそうですが、やりたかったことは、ベクトル命令のオペランドにオフセット付きアドレスを指定しないことです。
先程まで見てきたように、常にwin = falseにすれば目的を達成しているように見えます。しかし残念ながら常にオフセット付きアドレスを拒絶することになり、スカラ命令にも影響が出てしまいます。変更前と変更後のアセンブラを比較します。
変更前後のアセンブラ比較
--- b_before.s 2020-05-28 21:17:24.607184754 +0900
+++ b_after.s 2020-05-28 21:14:31.375142095 +0900
@@ -21,8 +21,10 @@
addi s0,sp,1200
.cfi_def_cfa 8, 0
addi a5,s0,-16
#★★スカラ命令なのにアドレスオペランドのオフセット設定が分解されている(この分割は本来不要)
- sw a5,-1188(s0)
- lw a5,-1188(s0)
+ addi a4,s0,-1188
+ sw a5,0(a4)
+ addi a5,s0,-1188
+ lw a5,0(a5)
addi a5,a5,-1168
addi a5,a5,255
srli a5,a5,8
@@ -35,7 +37,8 @@
# 0 "" 2
#NO_APP
#★★ベクトル命令のアドレスオペランドのオフセット設定が分解されるのは狙い通り
- vsw.v v0,256(a5)
+ addi a4,a5,256
+ vsw.v v0,0(a4)
.loc 1 9 2
addi a4,s0,-336
#APP
ベクトル命令は狙い通りですが、スカラ命令までアドレスオペランドのオフセット設定が分解されてしまいました。この分割は本来不要です。
これをどう抑えるかはまた次回。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月30日
GCCを調べる - その13-2 - オフセット付きアドレス全部禁止
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月29日の日記参照)メモリというかオフセット付きアドレスのconstraintをチェックしていそうな箇所を見つけました。
ベクトル命令の場合は、オフセット付きアドレスを拒否してほしいです。試しにwin = true; の部分をwin = false; に変更するとどんな動きをするでしょうか?
常にwin = falseにしたときの動作
// gcc/lra-constraints.c
static bool
process_alt_operands (int only_alternative)
{
...
for (nalt = 0; nalt < n_alternatives; nalt++) //★★基本的には全ての選択肢を検討するのだが、losersが0だとbreakする(ループ終端(1000行後)で判定している)
{
...
for (nop = 0; nop < n_operands; nop++)
{
...
costly_p = false;
do
{
switch ((c = *p, len = CONSTRAINT_LEN (c, p)), c)
{
...
default:
cn = lookup_constraint (p);
switch (get_constraint_type (cn))
{
...
case CT_MEMORY:
if (MEM_P (op)
&& satisfies_memory_constraint_p (op, cn)) //★★今回はこちら
win = false; //★★常にfalseにする
...
}
while ((p += len), c);
scratch_p = (operand_reg[nop] != NULL_RTX
&& lra_former_scratch_p (REGNO (operand_reg[nop])));
/* Record which operands fit this alternative. */
if (win) //★★不成立、this_alternative_winはfalseのまま
{
this_alternative_win = true;
...
}
else if (did_match)
this_alternative_match_win = true;
else
{
int const_to_mem = 0;
bool no_regs_p;
reject += op_reject;
...
/* If the operand is dying, has a matching constraint,
and satisfies constraints of the matched operand
which failed to satisfy the own constraints, most probably
the reload for this operand will be gone. */
if (this_alternative_matches >= 0
&& !curr_alt_win[this_alternative_matches]
&& REG_P (op)
&& find_regno_note (curr_insn, REG_DEAD, REGNO (op))
&& (hard_regno[nop] >= 0
? in_hard_reg_set_p (this_alternative_set,
mode, hard_regno[nop])
: in_class_p (op, this_alternative, NULL))) //★★不成立
{
...
}
else
{
/* Strict_low_part requires to reload the register
not the sub-register. In this case we should
check that a final reload hard reg can hold the
value mode. */
if (curr_static_id->operand[nop].strict_low
&& REG_P (op)
&& hard_regno[nop] < 0
&& GET_CODE (*curr_id->operand_loc[nop]) == SUBREG
&& ira_class_hard_regs_num[this_alternative] > 0
&& (!targetm.hard_regno_mode_ok
(ira_class_hard_regs[this_alternative][0],
GET_MODE (*curr_id->operand_loc[nop])))) //★★不成立
{
...
}
losers++; //★★この変数が0以外だと、続けて他の選択肢も検討される
}
...
if (MEM_P (op) && offmemok)
addr_losers++;
else
...
curr_alt[nop] = this_alternative;
curr_alt_set[nop] = this_alternative_set;
curr_alt_win[nop] = this_alternative_win; //★★false
curr_alt_match_win[nop] = this_alternative_match_win;
curr_alt_offmemok[nop] = this_alternative_offmemok;
curr_alt_matches[nop] = this_alternative_matches;
if (this_alternative_matches >= 0
&& !did_match && !this_alternative_win)
curr_alt_win[this_alternative_matches] = false;
if (early_clobber_p && operand_reg[nop] != NULL_RTX)
early_clobbered_nops[early_clobbered_regs_num++] = nop;
}
...
ok_p = true; //★★関数の返り値
curr_alt_dont_inherit_ops_num = 0;
...
/* If this alternative can be made to work by reloading, and it
needs less reloading than the others checked so far, record
it as the chosen goal for reloading. */
if ((best_losers != 0 && losers == 0)
|| (((best_losers == 0 && losers == 0)
|| (best_losers != 0 && losers != 0))
&& (best_overall > overall
|| (best_overall == overall
/* If the cost of the reloads is the same,
prefer alternative which requires minimal
number of reload regs. */
&& (reload_nregs < best_reload_nregs
|| (reload_nregs == best_reload_nregs
&& (best_reload_sum < reload_sum
|| (best_reload_sum == reload_sum
&& nalt < goal_alt_number))))))))
{
for (nop = 0; nop < n_operands; nop++)
{
goal_alt_win[nop] = curr_alt_win[nop]; //★★false
goal_alt_match_win[nop] = curr_alt_match_win[nop];
goal_alt_matches[nop] = curr_alt_matches[nop];
goal_alt[nop] = curr_alt[nop];
goal_alt_offmemok[nop] = curr_alt_offmemok[nop];
}
goal_alt_dont_inherit_ops_num = curr_alt_dont_inherit_ops_num;
for (nop = 0; nop < curr_alt_dont_inherit_ops_num; nop++)
goal_alt_dont_inherit_ops[nop] = curr_alt_dont_inherit_ops[nop];
goal_alt_swapped = curr_swapped;
best_overall = overall;
best_losers = losers;
best_reload_nregs = reload_nregs;
best_reload_sum = reload_sum;
goal_alt_number = nalt;
}
if (losers == 0) //★★最初の方のfor (nalt = 0; nalt < n_alternatives; nalt++) をbreakするかどうか決めてる
/* Everything is satisfied. Do not process alternatives
anymore. */
break;
fail:
;
}
return ok_p;
}
長ったらしくてわかりにくいですが、今回注目したい制御条件はwinに関係する部分です。
- this_alternative_winがfalse
- curr_alt_win[nop] がfalse(nop = 0のとき)
- goal_alt_win[nop] がfalse(nop = 0のとき)
関数process_alt_operands() の返り値はbool型で、falseは他のオペランドの選択肢はない、trueは他の選択肢があるという意味だそうです。今回はtrueを返します。だから何?と思いますが、あとでこの値がちょっとだけ出ます。
関数の最後に設定するgoal_alt_winというグローバル変数が、process_alt_operands() 関数の「外側」の制御に影響を及ぼします。これはひどい。良い子の皆さんはこういうコードを書いてはいけません。
今回注目しているinsnのオペランドは2つあり、nop = 0がメモリのオペランド、nop = 1がレジスタのオペランドです。デバッガで追いかけるとthis_ なんちゃらの値はそれぞれ下記のようになっていました。
各オペランドのwinの値
---------- nop = 0
op = (mem/c:V64SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 256 [0x100])) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
this_alternative = NO_REGS
this_alternative_set = {elts = {0, 0}}
this_alternative_win = false
this_alternative_match_win = false
this_alternative_offmemok = true
this_alternative_matches = -1
---------- nop = 1
op = (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
this_alternative = VP_REGS
this_alternative_set = {elts = {0, 4294967295}}
this_alternative_win = true
this_alternative_match_win = false
this_alternative_offmemok = false
this_alternative_matches = -1
似たような名前の変数this_, curr_, goal_ が3つ出てきます。勝ち抜き方式にして一番良い選択肢を残しているようです。一番内側のforループでthis_XX(ローカル変数)の値を作り、良さそうな値ならcurr_alt_XX配列(static変数)に代入します。curr_alt_ はどんどん上書きされ、最後に残った値がgoal_alt_XX配列(グローバル変数)に代入されます。
処理の骨組みだけ示すと下記のようになります。
goal_alt_XX[op] が決まる仕組み
process_alt_operands
{
for (nalt = 0; nalt < n_alternatives; nalt++) //★★選択肢の数だけループ
{
for (nop = 0; nop < n_operands; nop++) //★★オペランドの数だけループ
{
{
//★★this_XXを決める戦い
}
//★★this_XXが決められないなら、次のオペランドを処理
//★★選ばれしthis_XXがcurr_alt_XX[op] に保存(後の選択肢のほうがさらに良ければ上書きされる)
}
}
//★★curr_alt_XX[op] をgoal_alt_XX[op] に保存
}
最終的にgoal_alt_XXの値がどうなるかというと、
最終的なgoal_alt_XXの値
goal_alt = {NO_REGS, VP_REGS, }
goal_alt_win = {false, true, }
goal_alt_match_win = {false, false, }
goal_alt_offmemok = {true, false, }
goal_alt_matches = {-1, -1, }
関数process_alt_operands() の最後でブレークしてgoal_alt_XXの値をダンプしました。コードを追いかけて求めるのはかなり困難です……。
グローバル変数goal_alt_winを変更したことによる影響は、また次回。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月29日
GCCを調べる - その13-1 - オフセット付きアドレスを禁止する
目次: GCC
メモリからのロード、ストアに問題があるので、おそらくメモリ周りのconstraint指定が間違っていて、本来受け付けてはいけないオペランドまで受け付けていると思われますが、証拠を掴む方法が全くわかりません。
今回追加したdefine_expand, define_insnのうちdefine_expandはconstraintなし、define_insnはmという標準のconstraintを使っています。手がかりになりそうなconstraint mから追ってみます。メモリのconstraintは下記に定義があります。
constraint "m" の定義
// gcc/defaults.h
#ifndef TARGET_MEM_CONSTRAINT
#define TARGET_MEM_CONSTRAINT 'm'
#endif
// gcc/common.md
(define_memory_constraint "TARGET_MEM_CONSTRAINT"
"Matches any valid memory."
(and (match_code "mem")
(match_test "/* hogehoge */ memory_address_addr_space_p (GET_MODE (op), XEXP (op, 0),
MEM_ADDR_SPACE (op))"))) //★★ここに適当なコメントを入れる
メモリのconstraintは若干イレギュラーな定義で、アーキテクチャにより "m" 以外の文字になります(s390のみ "e" を使います)。RISC-VではTARGET_MEM_CONSTRAINTは "m" ですから、特に気にしなくて良いです。
定義の最後にあるmatch_testに続くコードに適当にコメントを入れて、ビルドしてからコメントの文字列でgrepすると、build_gcc/tm-constrs.hのsatisfies_constraint_m() という関数にコピペされていることがわかります。このルールはconstraint "m" だけでなく他も同じです。関数satisfies_constraint_(文字) が自動的に生成され、条件チェックされます。
この関数でブレークしたいですがstatic inlineになっておりブレークが掛からないので、適当にfor_break_tmp() 関数を一つ追加しておき、この関数で止めます。
constraint "m" の判定関数
// build_gcc/tm-constrs.h
static void for_break_tmp(rtx op) //★★関数を足す
{
}
static inline bool
satisfies_constraint_m (rtx op) //★★この関数にブレークは設定できないので…
{
for_break_temp(op); //★★関数呼び出しを足す
return (GET_CODE (op) == MEM) && (
#line 26 "./gcc/gcc/common.md"
( /* hogehoge */ memory_address_addr_space_p (GET_MODE (op), XEXP (op, 0),
MEM_ADDR_SPACE (op)))); //★★さっきいれた適当なコメントも一緒にコピーされる
}
無条件だと何度も止まって鬱陶しいので、machine modeで条件ブレークすると良いでしょう。
constraint "m" の判定関数でブレーク
(gdb) b for_break_tmp if op->mode == E_V64SImode
(gdb) r
Breakpoint 1, for_break_tmp (op=0x7ffff7bacab0) at tm-constrs.h:9
9 }
(gdb) bt
#0 for_break_tmp (op=0x7ffff7bacab0)
at tm-constrs.h:9
#1 0x000000000217dfa8 in satisfies_constraint_m (op=0x7ffff7bacab0)
at tm-constrs.h:13
#2 0x0000000000ebcc07 in constraint_satisfied_p (x=0x7ffff7bacab0, c=CONSTRAINT_m)
at ./tm-preds.h:108
#3 0x0000000000ebe8cf in satisfies_memory_constraint_p (op=0x7ffff7bacab0,
constraint=CONSTRAINT_m)
at ./gcc/gcc/lra-constraints.c:421
#4 0x0000000000ec7149 in process_alt_operands (only_alternative=-1)
at ./gcc/gcc/lra-constraints.c:2338
#5 0x0000000000eceb52 in curr_insn_transform (check_only_p=false)
at ./gcc/gcc/lra-constraints.c:3977
#6 0x0000000000ed4e71 in lra_constraints (first_p=true)
at ./gcc/gcc/lra-constraints.c:5027
#7 0x0000000000eacae4 in lra (f=0x454f640)
at ./gcc/gcc/lra.c:2437
#8 0x0000000000e1a557 in do_reload ()
at ./gcc/gcc/ira.c:5523
#9 0x0000000000e1af95 in (anonymous namespace)::pass_reload::execute (this=0x449fdf0)
at ./gcc/gcc/ira.c:5709
パスは282r.reloadです。いくつかスタックフレームを遡るとprocess_alt_operands() 関数にたどり着きます。ベクトルレジスタの追加(2020年3月29日の日記参照)のときに見ました、懐かしいですね。それはさておき下記のコードから呼ばれています。
constraint "m" を判定する箇所
static bool
process_alt_operands (int only_alternative)
{
...
costly_p = false;
do
{
switch ((c = *p, len = CONSTRAINT_LEN (c, p)), c)
{
...
default:
cn = lookup_constraint (p);
switch (get_constraint_type (cn))
{
case CT_REGISTER:
cl = reg_class_for_constraint (cn); //★★前回はこちらに来ていた
if (cl != NO_REGS)
goto reg;
break;
case CT_CONST_INT:
if (CONST_INT_P (op)
&& insn_const_int_ok_for_constraint (INTVAL (op), cn))
win = true;
break;
case CT_MEMORY:
if (MEM_P (op)
&& satisfies_memory_constraint_p (op, cn)) //★★今回はこちらに来る
win = true;
else if (spilled_pseudo_p (op))
win = true;
/* If we didn't already win, we can reload constants
via force_const_mem or put the pseudo value into
memory, or make other memory by reloading the
address like for 'o'. */
if (CONST_POOL_OK_P (mode, op)
|| MEM_P (op) || REG_P (op)
/* We can restore the equiv insn by a
reload. */
|| equiv_substition_p[nop])
badop = false;
constmemok = true;
offmemok = true;
break;
// opが指すRTLはこんな感じ
(mem/c:V64SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 256 [0x100])) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
渡されたRTLに対し、satisfies_memory_constraint_p() はconstraint "m" の条件と合致するか調べ、合致していたらwinフラグをtrueにしています。
この辺りを変えれば、オフセット付きアドレスに変化が起きそうです。続きはまた今度。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月28日
STATIONflowのバグ
目次: ゲーム
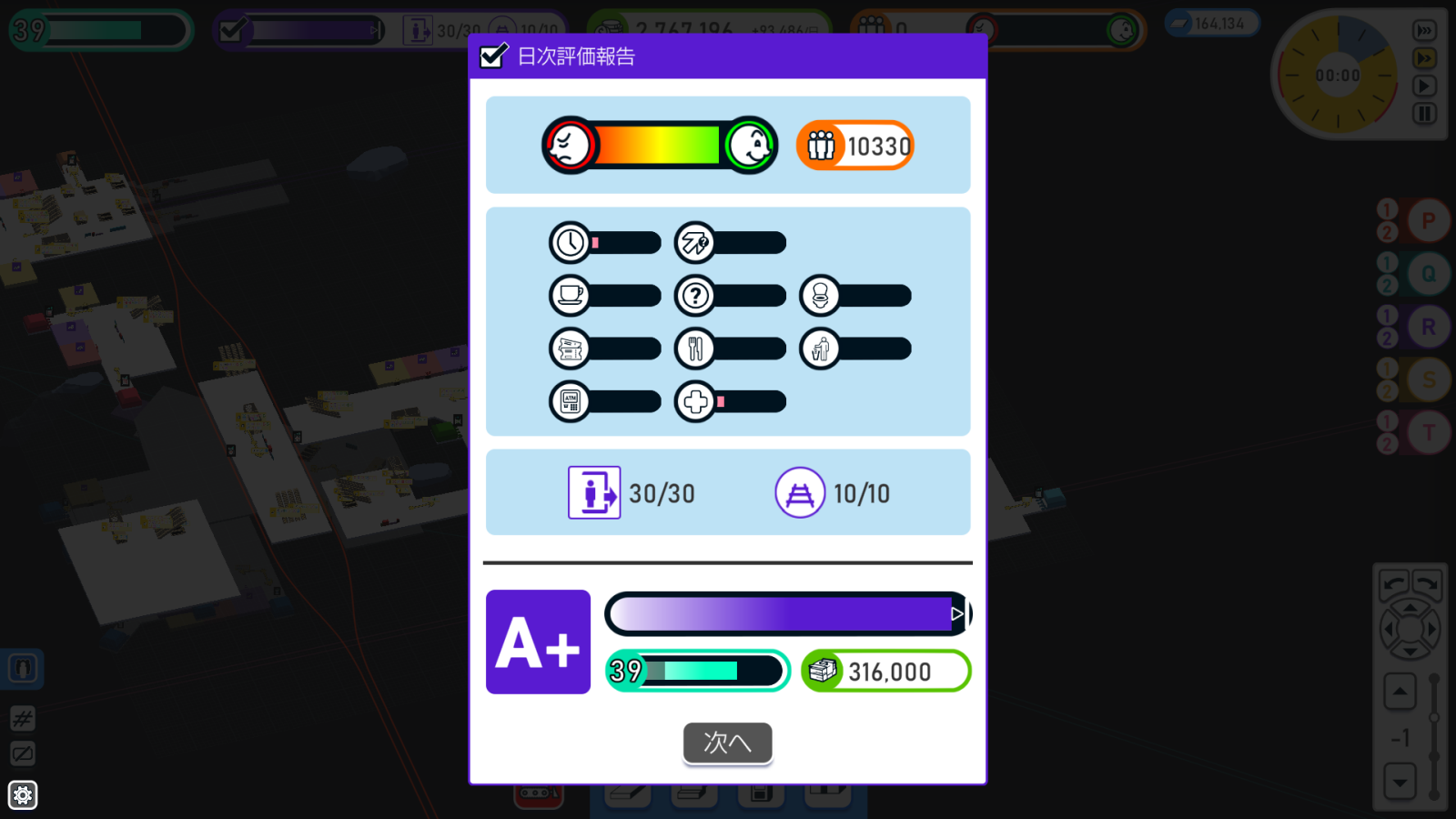
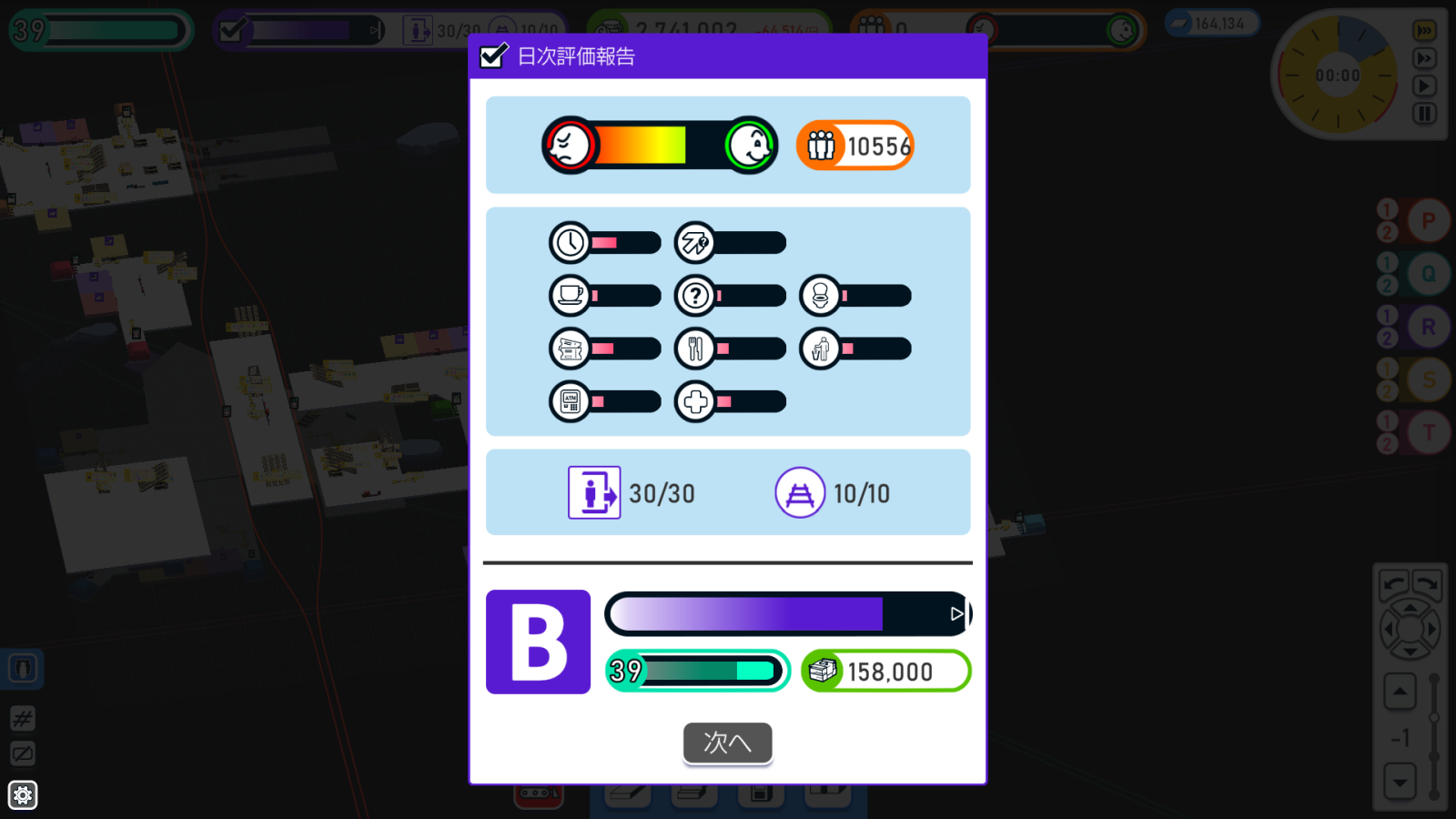
STATIONflowバグってますね……。ゲーム進行速度を最大にすると勝手に評価が下がってしまいます。これはあんまりだ。
ゲーム進行速度を最大の3にすると、評価がかなり下がります。速度1 or 2ならA+(1枚目)ですが、速度3だとB(2枚目)です。他は何も変えず、速度だけ変えた結果です。
STATIONflowは評価と収入が直結しており、評価が2段階下がると大赤字です。画像の右下が収入ですが、A+ 316000からB 158000に下がってますよね?
速度3のときの客の評価値を見ると、利用施設の待ち時間に対する評価が軒並み悪化しています。速度3だけ待ち時間の計算をミスってるんじゃないでしょうか?
あまりにも評価が乱高下するから、何が起きたのか結構悩んでしまいました。無駄に悩んだ時間を返せ。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月27日
STATIONflowランク20
目次: ゲーム
ゲーム進行的に1つの区切りと思われる、ランク20を超えました。駅が広くなるとちょっと困った現象が発生します。
現象としては終電が出た後に、極端に評価値が下がります。仕組みはこんな感じ。
- 終電が出る
- 電車を目的地にしていた客の目的地がなくなる
- 目的地がなくなった客が目的地を変える
- 偶然にも遠い目的地を選んだ客は長距離歩く羽目になる
- 評価値が下がる
この問題は常に発生していて、序盤は駅が狭いのと人が少ないので問題ありませんが、終盤は一気に1,000〜2,000人規模で目的地の切り替えが発生して、最終の評価値に影響するほど下がることがあります。
終電の時間は固定で、プレーヤーの努力でどうすることもできません。理不尽だ……。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月26日
GCCを調べる - その12-2 - ベクトル命令の出力(define_insn追加編)
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月25日の日記参照)にてdefine_insnを追加しましたが、エラーが出ました。引き続きエラーを見ます。
define_insnを追加後、エラーが起きている箇所
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
/* Return the appropriate instructions to move SRC into DEST. Assume
that SRC is operand 1 and DEST is operand 0. */
const char *
riscv_output_move (rtx dest, rtx src)
{
enum rtx_code dest_code, src_code;
machine_mode mode;
bool dbl_p;
...
if (dest_code == REG && FP_REG_P (REGNO (dest)))
{
if (src_code == MEM)
return dbl_p ? "fld\t%0,%1" : "flw\t%0,%1";
}
gcc_unreachable (); //★★ここに到達している
}
RTLに対応するアセンブラを出力する場所のようです。ベクトル型には当然対応していません。ひとまず浮動小数点のムーブ、ロード、ストアを真似して追加します。
ベクトル型のムーブ、ロード、ストアに対応する
// gcc/config/riscv/riscv.c
/* Return the appropriate instructions to move SRC into DEST. Assume
that SRC is operand 1 and DEST is operand 0. */
const char *
riscv_output_move (rtx dest, rtx src)
{
enum rtx_code dest_code, src_code;
machine_mode mode;
bool dbl_p;
...
if (src_code == REG && VP_REG_P (REGNO (src)))
{
if (dest_code == REG && VP_REG_P (REGNO (dest)))
return "vmv.v\t%0,%1"; //★★ムーブ
if (dest_code == MEM)
return "vsw.v\t%1,%0"; //★★ストア
}
if (dest_code == REG && VP_REG_P (REGNO (dest)))
{
if (src_code == MEM)
return "vlw.v\t%0,%1"; //★★ロード
}
gcc_unreachable ();
}
やっとエラーが出なくなりました。本当に長かったです。
サンプルコード
typedef int __v64si __attribute__((__vector_size__(256)));
void _start()
{
int b[100];
__v64si v1;
__asm__ volatile ("vlw.v %0, %1\n" : "=&v"(v1) : "A"(b[10]));
}
サンプルコードビルド、逆アセンブル
$ riscv32-unknown-elf-gcc -Wall -march=rv32gcv b.c -O0 -nostdlib -g
$ riscv32-unknown-elf-objdump -drS a.out
...
__asm__ volatile ("vlw.v %0, %1\n" : "=&v"(v1) : "A"(b[10]));
10076: e8840713 addi a4,s0,-376
1007a: 12076007 vlw.v v0,(a4)
1007e: 0207e027 vsw.v v0,(a5)
}
10082: 0001 nop
10084: 3ac12403 lw s0,940(sp)
10088: 3b010113 addi sp,sp,944
1008c: 8082 ret
それらしいバイナリも出力されています。
冒険はまだ続く
ベクトルレジスタが1つしか使用されていなくて寂しいので、サンプルコードを変更してvlw.vを複数書きます。するとまたエラーが出ます。
サンプルコード2
typedef int __v64si __attribute__((__vector_size__(256)));
void _start()
{
int b[100];
__v64si v1, v2;
__asm__ volatile ("vlw.v %0, %1\n" : "=&v"(v1) : "A"(b[10]));
__asm__ volatile ("vlw.v %0, %1\n" : "=&v"(v2) : "A"(b[20]));
}
サンプルコード2ビルドできず
$ riscv32-unknown-elf-gcc -Wall -march=rv32gcv b.c -O0 -nostdlib -g /tmp/ccsg5iId.s: Assembler messages: /tmp/ccsg5iId.s:38: Error: illegal operands `vsw.v v0,256(a5)'
コンパイラはエラーを出していませんが、アセンブラがエラーを出しています。どうも変なオペランドが出力されているようです。うーん、惜しい。アセンブラを見ると、
サンプルコード2アセンブラ
...
.loc 1 8 2
addi a4,s0,-376
#APP
# 8 "b.c" 1
vlw.v v0, 0(a4)
# 0 "" 2
#NO_APP
vsw.v v0,256(a5) #★★この命令でエラー(オフセットを使っている)
.loc 1 9 2
addi a4,s0,-336
#APP
# 9 "b.c" 1
vlw.v v0, 0(a4)
# 0 "" 2
#NO_APP
vsw.v v0,0(a5) #★★この命令はOK(オフセットを使っていない)
.loc 1 10 1
nop
lw s0,1196(sp)
...
スカラ演算用のlw, sw命令とオペランドの制約が異なり、vlw.v, vsw.v命令はオフセット付きアドレスをオペランドに取れません。コンパイラはオフセット付きアドレスをオペランドに出力しないように抑制する必要があります。続きはまた今度。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月25日
GCCを調べる - その12-1 - 続、オプションO0のエラー調査(define_insn追加編)
目次: GCC
引き続き、ベクトル型を使用する際の下記の問題に取り組みます。
- 最適化オプションをO0にするとコンパイラがinternal errorを出す
前回(2020年5月22日の日記、2020年5月23日の日記、2020年5月24日の日記参照)にてdefine_expandを追加し、Internal compile error: maximum number of generated reload insns per insn achieved (90) は出なくなりましたが、別のエラーが出ました。
define_expand追加後のエラー
b.c: In function '_start':
b.c:25:1: error: unrecognizable insn:
25 | }
| ^
(insn 10 11 0 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
during RTL pass: vregs
dump file: b.c.237r.vregs
b.c:25:1: internal compiler error: in extract_insn, at recog.c:2294
エラーの起きている箇所はvregというパスで、RTLのパスでは2番目(expandの次)です。序盤のパスですし、変なRTLが後ろのパスに伝わって意味不明なエラー、というケースではなさそうです。素直にエラーが出ている箇所を見ます。
エラーが起きている箇所
// gcc/recog.c
void
extract_insn (rtx_insn *insn)
{
int i;
int icode;
int noperands;
rtx body = PATTERN (insn);
...
switch (GET_CODE (body))
{
...
case SET:
if (GET_CODE (SET_SRC (body)) == ASM_OPERANDS)
goto asm_insn;
else
goto normal_insn; //★★ここにきて、ジャンプ
...
default:
normal_insn:
/* Ordinary insn: recognize it, get the operands via insn_extract
and get the constraints. */
icode = recog_memoized (insn);
if (icode < 0)
fatal_insn_not_found (insn); //★★ここでエラー
...
// gcc/recog.h
/* Try recognizing the instruction INSN,
and return the code number that results.
Remember the code so that repeated calls do not
need to spend the time for actual rerecognition.
This function is the normal interface to instruction recognition.
The automatically-generated function `recog' is normally called
through this one. */
static inline int
recog_memoized (rtx_insn *insn)
{
if (INSN_CODE (insn) < 0)
INSN_CODE (insn) = recog (PATTERN (insn), insn, 0);
return INSN_CODE (insn);
}
// ★★PATTERN(insn) はinsn->u.fld[3]->rt_rtxを返す。
PATTERN() の3という数値はinsnのRTL formatに基づいています。insnのRTLの引数は "uuBeiie" となっており、4つ目の引数eがinsnの実行したい処理を表しているようです。残念ながらPATTERN() という関数名から、そのような事情は掴めないですよね、普通。
insn RTLのe引数
|u |u|B|e ↓これ
(insn 10 11 0 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
続きを追います。recog() という関数に入っていきます。recogから始まる関数群は自動生成されたコードです。自動生成コードは読みにくいですが、GCC本体よりロジックがシンプルで理解しやすいです。GCC本体は読みにくい&理解不能なので、辛くて泣けてきます。
エラーが起きている箇所(続き)
// build_gcc/insn-recog.c
int
recog (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
rtx * const operands ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED = &recog_data.operand[0];
rtx x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9;
rtx x10, x11, x12, x13, x14, x15, x16, x17;
rtx x18, x19, x20, x21, x22, x23, x24, x25;
rtx x26, x27, x28;
int res ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED;
recog_data.insn = NULL;
switch (GET_CODE (x1))
{
case SET:
return recog_17 (x1, insn, pnum_clobbers); //★★これ
...
static int
recog_17 (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
rtx * const operands ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED = &recog_data.operand[0];
rtx x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7;
int res ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED;
x2 = XEXP (x1, 1);
switch (GET_CODE (x2))
{
...
case CONST_INT:
case CONST_WIDE_INT:
case CONST_POLY_INT:
case CONST_FIXED:
case CONST_DOUBLE:
case CONST_VECTOR:
case CONST:
case REG:
case SUBREG:
case MEM:
case LABEL_REF:
case SYMBOL_REF:
case HIGH:
return recog_7 (x1, insn, pnum_clobbers); //★★これ
...
static int
recog_7 (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
rtx * const operands ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED = &recog_data.operand[0];
rtx x2, x3, x4;
int res ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED;
x2 = XEXP (x1, 0);
switch (GET_CODE (x2))
{
case REG:
case SUBREG:
case MEM:
res = recog_2 (x1, insn, pnum_clobbers); //★★これ
if (res >= 0)
return res;
break;
...
static int
recog_2 (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
rtx * const operands ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED = &recog_data.operand[0];
rtx x2, x3, x4;
int res ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED;
x2 = XEXP (x1, 0);
operands[0] = x2;
x3 = XEXP (x1, 1);
operands[1] = x3;
switch (GET_MODE (operands[0]))
{
...
default:
break; //★★V64SImodeはいずれのcaseにも該当しないのでここにくる
}
...
if (pnum_clobbers == NULL //★★この条件に引っかかる
|| GET_CODE (x2) != MEM)
return -1; //★★ここにくる
...
なぜかrecog() 関数はデバッグ情報がおかしくて、gdbのnextコマンドが正常に動きません。非常にデバッグしづらいです。gdbで追うときはbuild_gcc/insn-recog.c内の #lineディレクティブを全て削除するとデバッグしやすいです。
エラーを解消するにはrecog_2のswitch-caseに変化を及ぼす方法を知る必要があります。しかしそんなものわかる訳ありません。仕方ないので周辺のコードを眺めます。
エラーが起きている箇所の周辺
static int
recog_2 (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
...
switch (GET_MODE (operands[0]))
{
case E_DImode:
if (nonimmediate_operand (operands[0], E_DImode)
&& move_operand (operands[1], E_DImode))
{
if (
#line 1340 "./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md" //★★この辺りにヒントがあるのでは??
(!TARGET_64BIT
&& (register_operand (operands[0], DImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], DImode))))
return 135; /* *movdi_32bit */
if (
#line 1350 "./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md"
(TARGET_64BIT
&& (register_operand (operands[0], DImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], DImode))))
return 136; /* *movdi_64bit */
}
break;
ぐちゃぐちゃのif文の中に #lineが差し込まれています。コードの一部をriscv.mdから持ってきているようです。
riscv.mdの該当部分
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md
(define_insn "*movdi_32bit"
[(set (match_operand:DI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "=r,r,r,m, *f,*f,*r,*f,*m")
(match_operand:DI 1 "move_operand" " r,i,m,r,*J*r,*m,*f,*f,*f"))]
★★↓このコードがrecog_2にコピーされている
"!TARGET_64BIT
&& (register_operand (operands[0], DImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], DImode))"
★★↑
{ return riscv_output_move (operands[0], operands[1]); }
[(set_attr "move_type" "move,const,load,store,mtc,fpload,mfc,fmove,fpstore")
(set_attr "mode" "DI")])
おそらくdefine_insnを定義すれば、recog_2() も変わるでしょう。近しいものをコピーして作ります。
riscv.mdにdefine_insnを追加
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md
(define_attr "vecmode" "unknown,V64SI"
(const_string "unknown"))
(define_insn "*movv64si_internal"
[(set (match_operand:V64SI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "=v,v,m")
(match_operand:V64SI 1 "move_operand" " v,m,v"))] //★★RTL template
"(register_operand (operands[0], V64SImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], V64SImode))" //★★condition
{ return riscv_output_move (operands[0], operands[1]); } //★★output template
[(set_attr "move_type" "move,load,store")
(set_attr "vecmode" "V64SI")]) //★★insn attributes
とりあえずRTL template, condition, insn attributesに出現するmachine modeだけ変更しました。これが合っているのかわかりませんが、ダメなら後で直しましょう。
define_insnを追加後のrecog
static int
recog_2 (rtx x1 ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
rtx_insn *insn ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
int *pnum_clobbers ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
...
switch (GET_MODE (operands[0]))
{
case E_V64SImode:
if (nonimmediate_operand (operands[0], E_V64SImode)
&& move_operand (operands[1], E_V64SImode)
&&
#line 1320 "./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md"
((register_operand (operands[0], V64SImode)
|| reg_or_0_operand (operands[1], V64SImode))))
return 134; /* *movv64si_internal */ //★★ここにくるようになった
break;
再びrecog_2() を追いかけてみると、先程はなかったcaseが増えており、-1ではない値が返されるようになりました。
define_insnを追加後のエラー
during RTL pass: final
dump file: b.c.314r.final
b.c: In function '_start':
b.c:25:1: internal compiler error: in riscv_output_move, at config/riscv/riscv.c:2000
25 | }
| ^
0x1ae3d41 riscv_output_move(rtx_def*, rtx_def*)
今度こそうまく行くかと思いきや、また別のエラーが発生しました。道のりは長そうです。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月24日
GCCを調べる - その11-3 - エラーを引き起こすRTLを回避する(define_expand追加編)
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月23日の日記参照)の続きです。エラーの原因となる代入操作RTLはemit_move_multi_word() で出力されており、条件の分岐点であるemit_move_insn_1() が怪しそうです。分岐条件を司るoptab_handler() を追います。
分岐条件の1つoptab_handler()
// build_gcc/insn-opinit.h
enum optab_tag {
unknown_optab,
sext_optab,
...
mov_optab,
...
// gcc/optabs-query.h
/* Return the insn used to implement mode MODE of OP, or CODE_FOR_nothing
if the target does not have such an insn. */
inline enum insn_code
optab_handler (optab op, machine_mode mode)
{
unsigned scode = (op << 16) | mode; //★★もしブレーク掛けたければop = mov_optab, mode = E_V64SImodeで引っ掛けられる
gcc_assert (op > LAST_CONV_OPTAB);
return raw_optab_handler (scode); //★★これ
}
// build_gcc/insn-opinit.c
enum insn_code
raw_optab_handler (unsigned scode)
{
int i = lookup_handler (scode); //★★これが -1だとCODE_FOR_nothingが返る
return (i >= 0 && this_fn_optabs->pat_enable[i]
? pats[i].icode : CODE_FOR_nothing);
}
static int
lookup_handler (unsigned scode)
{
int l = 0, h = ARRAY_SIZE (pats), m;
while (h > l)
{
m = (h + l) / 2;
if (scode == pats[m].scode)
return m;
else if (scode < pats[m].scode)
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return -1;
}
//★★pats[] の定義
struct optab_pat {
unsigned scode;
enum insn_code icode;
};
static const struct optab_pat pats[NUM_OPTAB_PATTERNS] = {
{ 0x010405, CODE_FOR_extendqihi2 },
{ 0x010406, CODE_FOR_extendqisi2 },
{ 0x010407, CODE_FOR_extendqidi2 },
{ 0x010505, CODE_FOR_extendhihi2 },
...
//★★this_fn_optabs->pat_enable[] を初期化しているコード
void
init_all_optabs (struct target_optabs *optabs)
{
bool *ena = optabs->pat_enable;
ena[0] = HAVE_extendqihi2;
ena[1] = HAVE_extendqisi2;
...
このlookup_handler() が -1を返すとemit_move_multi_word() を実行します。lookup_handler() はpatsという構造体を2分探索する単純な関数ですから、大事なのはpatsの中身と変更方法です。
ところがpatsをどうやって作るか?については、手がかりがありません。GCCはクソコードすぎて辛い。とりあえずCODE_FOR_ なんとか、という部分と、ena[] = HAVE_ の部分は自動生成コードっぽいですから、適当にキーワードを考えてgrepします。
patsの作り方を捜索
#### ChangeLogが良く引っかかってうざいので排除推奨
$ grep -r CODE_FOR_%s | grep -v ^ChangeLog
genopinit.c: fprintf (s_file, " { %#08x, CODE_FOR_%s },\n", p->sort_num, p->name);
gencodes.c: printf (",\n CODE_FOR_%s = CODE_FOR_nothing", name);
gencodes.c: printf (",\n CODE_FOR_%s = %d", name, info->index);
genemit.c: printf (" return CODE_FOR_%s;\n", instance->name);
gentarget-def.c: printf ("#undef TARGET_CODE_FOR_%s\n", upper_name);
gentarget-def.c: printf ("#define TARGET_CODE_FOR_%s ", upper_name);
gentarget-def.c: printf ("CODE_FOR_%s\n", name);
$ grep -r HAVE_ | grep 'ena\[' | grep -v ^ChangeLog
genopinit.c: fprintf (s_file, " ena[%u] = HAVE_%s;\n", i, p->name);
コードの形と見比べるとgenopinit.cがpatsの作成者で間違いなさそうです。このプログラムはcc1の一部ではなく、補助ツールgenopinitのコードです。ツールの使い方がわからないのでビルドログを見ます。
genopinitの使い方
# build_gcc/Makefile
s-opinit: $(MD_DEPS) build/genopinit$(build_exeext) insn-conditions.md
$(RUN_GEN) build/genopinit$(build_exeext) $(md_file) \
insn-conditions.md -htmp-opinit.h -ctmp-opinit.c
# ビルドログ
build/genopinit ./gcc/gcc/common.md ./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md \
insn-conditions.md -htmp-opinit.h -ctmp-opinit.c
いくつか *.mdファイルを指定するだけです。genopinitのmain() 関数を見ると、2つの条件DEFINE_INSNもしくはDEFINE_EXPANDのときだけ gen_insn() を呼びます。
genopinitのmain関数
// gcc/genopinit.c
int
main (int argc, const char **argv)
{
FILE *h_file, *s_file;
unsigned int i, j, n, last_kind[5];
optab_pattern *p;
progname = "genopinit";
if (NUM_OPTABS > 0xffff || MAX_MACHINE_MODE >= 0xff)
fatal ("genopinit range assumptions invalid");
if (!init_rtx_reader_args_cb (argc, argv, handle_arg))
return (FATAL_EXIT_CODE);
h_file = open_outfile (header_file_name);
s_file = open_outfile (source_file_name);
/* Read the machine description. */
md_rtx_info info;
while (read_md_rtx (&info))
switch (GET_CODE (info.def))
{
case DEFINE_INSN:
case DEFINE_EXPAND:
gen_insn (&info); //★★これ
break;
default:
break;
}
/* Sort the collected patterns. */
patterns.qsort (pattern_cmp);
...
この記事を読むような方は、既に何を変更すれば良いかご存知かもしれませんが、せっかくなのでgenopinitの動きを追います。gen_insn() にブレークを掛けて、DEFINE_INSNとDEFINE_EXPANDのときに何が起きるのか見ます。
genopinitの動きを観察(DEFINE_INSN)
$ gdb build_gcc/build/genopinit
(gdb) b gen_insn
Breakpoint 1 at 0x402920: file ./gcc/gcc/genopinit.c, line 45.
(gdb) r common.md config/riscv/riscv.md build_gcc/insn-conditions.md -hhhh -cccc
Breakpoint 1, gen_insn (info=0x7fffffffd970)
at ./gcc/gcc/genopinit.c:45
45 if (find_optab (&p, XSTR (info->def, 0)))
(gdb) p *info
$3 = {
def = 0x4bc030,
loc = {
filename = 0x7fffffffde93 "config/riscv/riscv.md", ★★ファイル名
lineno = 431, ★★行番号
colno = 1
},
index = 1
}
(gdb) p info->def->code
$5 = DEFINE_INSN
genopinitの動きを観察(DEFINE_INSN)
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md:431
★★*.mdファイルのdefine_insnと紐付いている
(define_insn "add<mode>3"
[(set (match_operand:ANYF 0 "register_operand" "=f")
(plus:ANYF (match_operand:ANYF 1 "register_operand" " f")
(match_operand:ANYF 2 "register_operand" " f")))]
"TARGET_HARD_FLOAT"
"fadd.<fmt>\t%0,%1,%2"
[(set_attr "type" "fadd")
(set_attr "mode" "<UNITMODE>")])
残ったのはDEFINE_EXPANDです。DEFINE_INSNでは止まってほしくないので、こういうときは条件付きブレークが便利です。
genopinitの動きを観察(DEFINE_EXPAND)
(gdb) b gen_insn if info->def->code == DEFINE_EXPAND
Note: breakpoint 1 also set at pc 0x402920.
Breakpoint 2 at 0x402920: file ./gcc/gcc/genopinit.c, line 45.
(gdb) c
Breakpoint 2, gen_insn (info=0x7fffffffd970)
at ./gcc/gcc/genopinit.c:45
45 if (find_optab (&p, XSTR (info->def, 0)))
(gdb) p *info
$6 = {
def = 0x4c4ef0,
loc = {
filename = 0x7fffffffde93 "config/riscv/riscv.md", ★★ファイル名
lineno = 635, ★★行番号
colno = 1
},
index = 352
}
genopinitの動きを観察(DEFINE_EXPAND)
;; gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md:635
★★*.mdファイルのdefine_expandと紐付いている
(define_expand "<u>mulditi3"
[(set (match_operand:TI 0 "register_operand")
(mult:TI (any_extend:TI (match_operand:DI 1 "register_operand"))
(any_extend:TI (match_operand:DI 2 "register_operand"))))]
"TARGET_MUL && TARGET_64BIT"
{
rtx low = gen_reg_rtx (DImode);
emit_insn (gen_muldi3 (low, operands[1], operands[2]));
rtx high = gen_reg_rtx (DImode);
emit_insn (gen_<u>muldi3_highpart (high, operands[1], operands[2]));
emit_move_insn (gen_lowpart (DImode, operands[0]), low);
emit_move_insn (gen_highpart (DImode, operands[0]), high);
DONE;
})
つまり *.mdファイルにdefine_expandもしくはdefine_insnを定義すればpatsの中身が増えてlookup_handler() に引っかかるはずです。riscv.mdに既に存在するmovsiやmovdiを真似して追加します。
define_expandを追加
;; config/riscv/riscv.md
(define_expand "movv64si"
[(set (match_operand:V64SI 0 "")
(match_operand:V64SI 1 ""))]
""
{
if (riscv_legitimize_move (V64SImode, operands[0], operands[1])) //★★この呼び出しは正しいかわからないが、とりあえずそのまま
DONE;
})
実行してみると、先程追加したコードが引っかかってifの条件が成立し、emit_insn() が呼び出されます。念のためにコードを再掲します。
分岐条件の1つoptab_handler()(再掲)
// gcc/expand.c
rtx_insn *
emit_move_insn_1 (rtx x, rtx y)
{
machine_mode mode = GET_MODE (x);
enum insn_code code;
gcc_assert ((unsigned int) mode < (unsigned int) MAX_MACHINE_MODE);
code = optab_handler (mov_optab, mode);
if (code != CODE_FOR_nothing) //★★CODE_FOR_nothingになるのが怪しい
return emit_insn (GEN_FCN (code) (x, y)); //★★こっちに行けばいいのだろうか??
...
// build_gcc/insn-opinit.h
/* Given an enum insn_code, access the function to construct
the body of that kind of insn. */
#define GEN_FCN(CODE) (insn_data[CODE].genfun)
実行してemit_move_insn_1() でブレークし、gdbで値をダンプすると下記のようになっているはずです。gen_movv64si() 関数が突然出てきますが、これは自動生成された関数です。
define_expand追加後のcode
(gdb) p code
$4 = CODE_FOR_movv64si ★★nothingからV64SIに変わった
(gdb) p insn_data[code].genfun
$5 = {func = 0x216ecea <gen_movv64si(rtx_def*, rtx_def*)>}
(gdb) p insn_data[code]
$6 = {
name = 0x2d764ed "movv64si",
output = {
single = 0x0,
multi = 0x0,
function = 0x0
},
genfun = {
func = 0x216eec5 <gen_movv64si(rtx_def*, rtx_def*)>
},
operand = 0x2d73ef0 <operand_data+10512>,
n_generator_args = 2 '\002',
n_operands = 2 '\002',
n_dups = 0 '\000',
n_alternatives = 0 '\000',
output_format = 0 '\000'
}
define_expand追加後に生成された関数gen_movv64si()
// build_gcc/insn-emit.c
/* ./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md:1308 */
rtx
gen_movv64si (rtx operand0,
rtx operand1)
{
rtx_insn *_val = 0;
start_sequence ();
{
rtx operands[2];
operands[0] = operand0;
operands[1] = operand1;
#define FAIL return (end_sequence (), _val)
#define DONE return (_val = get_insns (), end_sequence (), _val)
#line 1312 "./gcc/gcc/config/riscv/riscv.md"
{
if (riscv_legitimize_move (V64SImode, operands[0], operands[1])) //★★この呼び出しは正しい?
DONE;
}
#undef DONE
#undef FAIL
operand0 = operands[0];
(void) operand0;
operand1 = operands[1];
(void) operand1;
}
emit_insn (gen_rtx_SET (operand0,
operand1));
_val = get_insns ();
end_sequence ();
return _val;
}
近くにあったdefine_expand("movdi") をコピーして作ったので、riscv_legitimize_move() を呼んでいますが、この実装が正しいかどうか今はわかりません。動作がおかしいようなら、後で調べたり、直したりする必要があるかもしれません。
現状、生成されたRTLを見た限りsetのdestination側のmachine modeがmem/c:SIからmem/c:V64SIに変わっていますし、問題なさそうに見えます。
define_expand追加後の236r.expand
(insn 11 7 10 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1
") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 99 virtual-stack-vars)
(const_int -360 [0xfffffffffffffe98])) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
(insn 10 11 0 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
;;★★(参考)define_expand追加前のRTL
(insn 10 74 11 2 (set (mem/c:SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S4 A2048])
(subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 0)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
しかし残念ながらdefine_expandの追加だけではダメで、変更後はこんなエラーが出ます。
define_expand追加後のエラー
b.c: In function '_start':
b.c:25:1: error: unrecognizable insn:
25 | }
| ^
(insn 10 11 0 2 (set (mem/c:V64SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S256 A2048])
(reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
during RTL pass: vregs
dump file: b.c.237r.vregs
b.c:25:1: internal compiler error: in extract_insn, at recog.c:2294
続きはまた次回。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月23日
GCCを調べる - その11-2 - オプションO0のエラーを引き起こすRTL(define_expand追加編)
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月22日の日記参照)の続きです。エラーの原因となる代入操作RTLはどこから出てきているのでしょう。RTLを遡っていくとexpandから出力されていることがわかります。expandはRTLの最初のパスで、GIMPLEからRTLに変換するためのパス(パス番号236)です。最初から間違っているということですね。
236r.expand
;;★★asm文に相当する箇所
(insn 74 7 10 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1
") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 99 virtual-stack-vars)
(const_int -360 [0xfffffffffffffe98])) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
;;★★自動的に出力される代入操作らしきRTL
(insn 10 74 11 2 (set (mem/c:SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S4 A2048])
(subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 0)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
(insn 11 10 12 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 4 [0x4])) [1 v1+4 S4 A32])
(subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 4)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
(insn 12 11 13 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 8 [0x8])) [1 v1+8 S4 A64])
(subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 8)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
...
ベクトル型V64SIのまま処理してほしいのに、4バイトごとに分割されて代入処理されています。この分割はどこで行われているか調べます。GCCはinsn RTLを出力するときは必ずemit_insn() という関数で出力することを利用します。
- 代入操作の先頭のinsnはUID 10です。ダンプファイルで確認するならinsnの隣にある数字(insn '10' ←これ74 11 2 …)がUIDです。
- emit_insn() を書き換えて、INSN_UID(x) == 10のときに適当に作った関数hoge() に飛ばすようにします。
- gdbで関数hoge() にブレークを掛けると、ちょうど目当てのRTLを出力した瞬間に実行が止まります。
ブレークで実行が止まったら、バックトレースを取れば呼び出しまでの経路がわかります。
代入操作の先頭insnを出力したときのバックトレース
(gdb) bt
#0 hoge () at ./gcc/gcc/emit-rtl.c:5103
#1 0x000000000097ebf9 in emit_insn (x=0x7ffff7aaa400)
at ./gcc/gcc/emit-rtl.c:5118
#2 0x00000000009ff017 in emit_move_insn_1 (x=0x7ffff7bada80, y=0x7ffff7bada98)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:3754
#3 0x00000000009ffa28 in emit_move_insn (x=0x7ffff7bada80, y=0x7ffff7bada98)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:3858
★★↓いかにも分割していそうな、怪しい名前
#4 0x00000000009fee38 in emit_move_multi_word (mode=E_V64SImode, x=0x7ffff7bada68, y=0x7ffff7bada50)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:3720
#5 0x00000000009ff505 in emit_move_insn_1 (x=0x7ffff7bada68, y=0x7ffff7bada50)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:3791
#6 0x00000000009ffa28 in emit_move_insn (x=0x7ffff7bada68, y=0x7ffff7bada50)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:3858
#7 0x0000000000a0cc8d in store_expr (exp=0x7ffff7ffb480, target=0x7ffff7bada68, call_param_p=0,
nontemporal=false, reverse=false)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:5932
#8 0x0000000000a09064 in expand_assignment (to=0x7ffff7aa7750, from=0x7ffff7ffb480, nontemporal=false)
at ./gcc/gcc/expr.c:5517
#9 0x000000000076c911 in expand_asm_stmt (stmt=0x7ffff7b8f4e0)
at ./gcc/gcc/cfgexpand.c:3198
#10 0x000000000076f89a in expand_gimple_stmt_1 (stmt=0x7ffff7b8f4e0)
at ./gcc/gcc/cfgexpand.c:3685
#11 0x00000000007705f0 in expand_gimple_stmt (stmt=0x7ffff7b8f4e0)
at ./gcc/gcc/cfgexpand.c:3853
#12 0x000000000077e7f1 in expand_gimple_basic_block (bb=0x7ffff7aba2d8, disable_tail_calls=false)
at ./gcc/gcc/cfgexpand.c:5893
#13 0x0000000000781a25 in (anonymous namespace)::pass_expand::execute (this=0x449bbf0, fun=0x7ffff7baa000)
バックトレースの中に怪しい名前の関数emit_move_multi_word() があります。いかにも複数のinsnを出力しそうな名前です。emit_move_multi_wordまでを追うと、下記のような経路を辿っています。
代入が分割されるところ
// gcc/cfgexpand.c
static void
expand_asm_stmt (gasm *stmt)
{
...
for (i = 0; i < noutputs; ++i)
{
tree val = output_tvec[i];
tree type = TREE_TYPE (val);
bool is_inout, allows_reg, allows_mem, ok;
rtx op;
...
if ((TREE_CODE (val) == INDIRECT_REF && allows_mem)
|| (DECL_P (val)
&& (allows_mem || REG_P (DECL_RTL (val)))
&& ! (REG_P (DECL_RTL (val))
&& GET_MODE (DECL_RTL (val)) != TYPE_MODE (type)))
|| ! allows_reg
|| is_inout
|| TREE_ADDRESSABLE (type))
{
...
}
else
{
op = assign_temp (type, 0, 1);
op = validize_mem (op);
if (!MEM_P (op) && TREE_CODE (val) == SSA_NAME)
set_reg_attrs_for_decl_rtl (SSA_NAME_VAR (val), op);
generating_concat_p = old_generating_concat_p;
push_to_sequence2 (after_rtl_seq, after_rtl_end);
expand_assignment (val, make_tree (type, op), false); //★★これ
after_rtl_seq = get_insns ();
after_rtl_end = get_last_insn ();
end_sequence ();
}
// gcc/expr.c
/* Expand an assignment that stores the value of FROM into TO. If NONTEMPORAL
is true, try generating a nontemporal store. */
void
expand_assignment (tree to, tree from, bool nontemporal)
{
...
/* Compute FROM and store the value in the rtx we got. */
push_temp_slots ();
result = store_expr (from, to_rtx, 0, nontemporal, false); //★★これ
preserve_temp_slots (result);
pop_temp_slots ();
return;
}
rtx_insn *
emit_move_insn (rtx x, rtx y)
{
machine_mode mode = GET_MODE (x);
rtx y_cst = NULL_RTX;
rtx_insn *last_insn;
rtx set;
...
last_insn = emit_move_insn_1 (x, y); //★★これ
if (y_cst && REG_P (x)
&& (set = single_set (last_insn)) != NULL_RTX
&& SET_DEST (set) == x
&& ! rtx_equal_p (y_cst, SET_SRC (set)))
set_unique_reg_note (last_insn, REG_EQUAL, copy_rtx (y_cst));
return last_insn;
}
rtx_insn *
emit_move_insn_1 (rtx x, rtx y)
{
machine_mode mode = GET_MODE (x);
enum insn_code code;
gcc_assert ((unsigned int) mode < (unsigned int) MAX_MACHINE_MODE);
code = optab_handler (mov_optab, mode);
if (code != CODE_FOR_nothing) //★★CODE_FOR_nothingになるのが怪しい
return emit_insn (GEN_FCN (code) (x, y)); //★★こっちに行けばいいのだろうか??
/* Expand complex moves by moving real part and imag part. */
if (COMPLEX_MODE_P (mode))
return emit_move_complex (mode, x, y); //★★もしくはこっち??
...
return emit_move_multi_word (mode, x, y); //★★この関数が呼ばれ、分割される
}
せっかく辿っておいてこんなこというのは若干気が引けますが、なぜこの経路を辿るのか?コードを見ても全くわかりません。特にexpand_asm_stmt() からemit_move_insn() までは、各関数が非常に長く、訳のわからないif文が山ほどあります。GCCってどうして動いてるんでしょうね?大丈夫?これ??
GCCのコードの酷さはさておき、emit_move_multi_word() と他の関数への分岐点になっている、emit_move_insn_1() が怪しそうです。次回以降、この関数を中心に調べます。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月22日
GCCを調べる - その11-1 - オプションO0のエラー調査(define_expand追加編)
目次: GCC
前回(2020年5月16日の日記、2020年5月17日の日記参照)の取り組みでインラインアセンブラでベクトル型を指定できるようになりましたが、下記の問題が残っていました。
- 最適化オプションをO0にするとコンパイラがinternal errorを出す
いよいよコンパイラがInternal compile errorを出す問題に取り組みます。ベクトル型を使ったインラインアセンブラをO0でコンパイルすると、下記のようなエラーメッセージが出ます。
O0のときのエラーメッセージ
b.c: In function '_start':
b.c:25:1: internal compiler error: maximum number of generated reload insns per insn achieved (90)
25 | }
| ^
このエラーが出るパスはreloadです。問題のある箇所に当たりをつけるため、O0のreloadと、1つ前のパスiraのRTLを比べます。
O0の281r.ira
;;★★asm文
(insn 74 7 10 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -360 [0xfffffffffffffe98])) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
;;★★スタックへの退避かな?
(insn 10 74 11 2 (set (mem/c:SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S4 A2048])*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 11 10 12 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 4 [0x4])) [1 v1+4 S4 A32])*movsi_internal
(nil))
...
O0の282r.reload
;;★★asm文
(insn 74 147 146 2 (set (reg:V64SI 112 [orig:109 v1 ] [109])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (reg:SI 113) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
(insn 146 74 236 2 (clobber (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
;;★★変なinsnが大量に増えている(ここから)
(insn 236 146 235 2 (set (reg:SI 202)*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 235 236 234 2 (set (reg:SI 201)*movsi_internal
(nil))
...
(insn 144 143 145 2 (set (subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 248)*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 145 144 10 2 (set (subreg:SI (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ]) 252)*movsi_internal
(nil))
;;★★変なinsnが大量に増えている(ここまで)
;;★★スタックへの退避かな?
(insn 10 145 11 2 (set (mem/c:SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S4 A2048])*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 11 10 12 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 4 [0x4])) [1 v1+4 S4 A32])*movsi_internal
(nil))
...
どうやらasm文の後に出てくる代入操作らしきRTLを処理しようとすると死んでしまうようです。次にO2とO0の違いを調べます。パスreloadより前に実行され、なおかつO0とO2双方で共通のパスはiraですから、iraのRTLを比較します。
O2とO0のときの281r.ira
;;★★O2のとき
(insn 73 7 204 2 (set (reg:V64SI 105 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -360 [0xfffffffffffffe98])) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(expr_list:REG_UNUSED (reg:V64SI 105 [ v1 ])
(nil)))
(debug_insn 204 73 203 2 (var_location:V64SI D#65 (clobber (const_int 0 [0]))) -1
(nil))
(debug_insn 203 204 202 2 (var_location:SI D#64 (subreg:SI (debug_expr:V64SI D#65) 0)) -1
(nil))
(debug_insn 202 203 201 2 (var_location:SI D#63 (subreg:SI (debug_expr:V64SI D#65) 4)) -1
(nil))
;;★★O0のとき
(insn 74 7 10 2 (set (reg:V64SI 109 [ v1 ])
(asm_operands/v:V64SI ("vlw.v %0, %1") ("=&v") 0 [
(mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 97 frame)
(const_int -360 [0xfffffffffffffe98])) [1 b+40 S4 A64])
]
[
(asm_input:SI ("A") b.c:7)
]
[] b.c:7)) "b.c":7:2 -1
(nil))
(insn 10 74 11 2 (set (mem/c:SI (reg/f:SI 108) [1 v1+0 S4 A2048])*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 11 10 12 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 4 [0x4])) [1 v1+4 S4 A32])*movsi_internal
(nil))
(insn 12 11 13 2 (set (mem/c:SI (plus:SI (reg/f:SI 108)
(const_int 8 [0x8])) [1 v1+8 S4 A64])*movsi_internal
(nil))
結論から先に言えばO2でもO0でも問題のあるRTLが生成されていると考えられます。RTLの所見をまとめると、
- O2もO0も似たような代入操作と思しきRTLが出力されています。
- O2の場合は代入操作が243r.fwprop1で消されます。
- O2もO0もfwprop1より前のRTLはほぼ同じです。
O2でInternal compile errorが発生しないのはラッキーに過ぎなかったようです。次回は問題となるRTLがどこから来るのか調べます。
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
2020年5月21日
さようならSeaMonkey
目次: ブラウザー/メーラー
かつてのMozillaのころからずっと使っていたSeaMonkeyですが、最近のサイトだと知らない子扱いされて悲しいのと、Cookieの削除がしづらくてたまらないので、ブラウザをFirefoxに変えました。
SeaMonkey今までありがとう。大変お世話になりました。
こんにちはFirefox
ブラウザに限らず、あまりアプリケーションのカスタマイズはしない方ですが、今のWindows版Firefoxは1点だけ嫌なところがあります。Ctrl+Tabを押したときにタブの一覧が出る挙動です。
Windowsのウインドウ切り替えと似ていますが、ブラウザのタブは元から横一直線に並んでいるので、リストを出す必要はないです。隣のタブに迅速に切り替えてほしい。
調べてみるとbrowser.ctrlTab.recentlyUsedOrderをfalseにすると Ctrl+Tabを押した瞬間に隣のタブに移る挙動に戻せることを知りました。とても嬉しい。これだよこれ!
コメント一覧
- コメントはありません。
 この記事にコメントする
この記事にコメントする
| < | 2020 | > | ||||
| << | < | 06 | > | >> | ||
| 日 | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 |
| - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | - | - | - | - |
こんてんつ
 wiki
wiki Linux JM
Linux JM Java API
Java API過去の日記
 2002年
2002年 2003年
2003年 2004年
2004年 2005年
2005年 2006年
2006年 2007年
2007年 2008年
2008年 2009年
2009年 2010年
2010年 2011年
2011年 2012年
2012年 2013年
2013年 2014年
2014年 2015年
2015年 2016年
2016年 2017年
2017年 2018年
2018年 2019年
2019年 2020年
2020年 2021年
2021年 2022年
2022年 2023年
2023年 2024年
2024年 2025年
2025年 2026年
2026年 過去日記について
過去日記についてその他の情報
 アクセス統計
アクセス統計 サーバ一覧
サーバ一覧 サイトの情報
サイトの情報合計:
本日:
 未来から過去へ表示(*)
未来から過去へ表示(*)